Space-IX
Interconnection for satellite operators

Global digital infrastructure is evolving – and its next stage of development lies in space. Satellite constellations in low Earth orbit (LEO) are opening up new possibilities to make data flows accessible worldwide, regardless of location or end-user connectivity.
What still feels visionary today is already beginning to take shape. First applications are emerging that link satellite connectivity with terrestrial networks – for example, to deliver broadband to remote regions or to strengthen mobile networks.
To make this evolution a reality, powerful and specialized interconnection infrastructure is needed – a Space-IX.

Wherever networks emerge, Interconnection will follow.
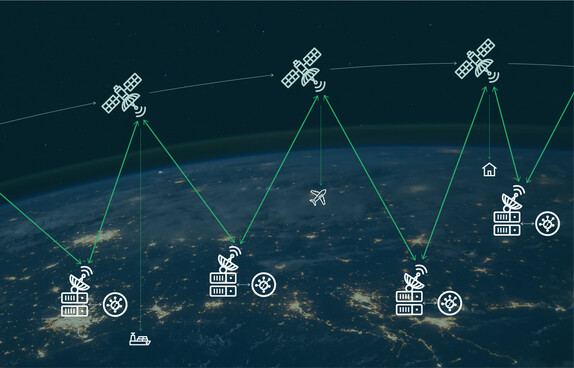
From GPS and mobile phones to traffic lights – life on Earth is increasingly dependent on technologies in Earth orbit. Yet the full potential of space remains largely untapped. On Earth, Internet Exchanges (IXs) serve as the hubs of digital communication. What works on the ground is now envisioned for orbit as well.
With Space-IX, DE-CIX envisions an Internet Exchange designed specifically for satellite networks in low Earth orbit. The goal: to enable intelligent interconnection between LEO satellites and ensure efficient integration with terrestrial infrastructure, cloud platforms, and content providers.
This vision builds on what is already becoming reality: DE-CIX integrates LEO satellite Internet service providers into existing interconnection ecosystems, unlocking new possibilities for broadband access, mobile backhaul, and edge connectivity.
An orbital network that is flexible, secure, and scalable – ushering in a new dimension of global digital infrastructure.
“Raw materials, tourism or national interests – whatever goals humanity pursues beyond the stratosphere, high-performance connectivity is the basis for achieving them. Developing an Internet Exchange in space will become necessary step in this direction.”